Cybersecurity Snapshot: AI Security Skills Drive Up Cyber Salaries, as Cyber Teams Grow Arsenal of AI Tools, Reports Find

Want recruiters to show you the money? A new report says AI skills are your golden ticket. Plus, cyber teams are all in on AI, including agentic AI tools. Oh, and please patch a nasty Oracle zero-day bug ASAP. And get the latest on vulnerability management, IoT security and cyber fraud.
Key takeaways
- Eager to stand out when seeking your next cyber job? Robert Half says one way is to become skilled at using AI for vulnerability management and other cyber tasks.
- On a related note, PwC is reporting that the use of AI for cyber defenses continues to grow, including agentic AI tools.
- Attackers are exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in Oracle’s E-Business Suite (EBS), so install the update with the fix now.
Here are six things you need to know for the week ending October 10.
1 - Report: Cyber pros with AI security skills are in high demand
Looking to give your cybersecurity career and salary a boost? Develop AI security skills.
The intel comes from Robert Half’s recently-released “2026 Salary Guide.” If you know how to use AI for things like managing vulnerabilities, automating security, or hunting for threats, you're going to be "highly sought."
“Many employers look for candidates who can work with AI programs or models, such as neural networks and natural language processing, for predicting and mitigating cyber risks,” Robert Half wrote in an article about the guide titled “What to Know About Hiring and Salary Trends in Cybersecurity.”
Cyber hiring managers are also eager for candidates with AI-related certifications, like Microsoft’s AI-900 and Google Cloud’s Machine Learning Engineer.
Of course, AI skills aren’t the only game in town. Having experience in these areas will also make your resume shine:
- Cloud security
- Data security
- DevSecOps
- Ethical hacking
- Network security
- Risk management
Having certain credentials also makes you a more attractive candidate for hiring managers, including:
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
- Certified Data Privacy Solutions Engineer (CDPSE)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- CompTIA Security+

Just remember to work on your people skills, too. The report reminds us that things like good communication and critical thinking are critical for cybersecurity roles.
And here’s Robert Half’s average salaries for “midpoint” cyber pros – meaning, those with a moderate amount of experience in these roles who meet most requirements and may possess relevant certifications:
- Cybersecurity analyst: $122,250
- Cybersecurity engineer: $144,000
- Data security analyst: $149,500
- Network security administrator: $130,000
- Network security engineer: $145,500
- Security architect: $157,250
- Systems security administrator: $134,750
- Systems security manager: $172,500
- CISO: $220,750
Bottom line: It’s a good time to be in cyber: 53% of U.S. employers are willing to open their wallets wider for candidates with the right skills.
To get more details, check out:
- Robert Half’s full “2026 Salary Guide”
- The report's section on technology salaries, where you can find the cybersecurity salary ranges for various roles
- The announcement “Robert Half Releases 2026 Salary Guide Highlighting Key Compensation Trends Amid a Complex Job Market”
2 - PwC: Cyber teams can’t get enough AI
Organizations are leaning heavily into AI to beef up their cyber defenses, including by prioritizing the use of agentic AI tools that can execute tasks with minimal human guidance.
That’s a key — albeit not unsurprising — discovery from PwC’s new “2026 Global Digital Trust Insights: C-suite playbook and findings” report, based on a global survey of almost 4,000 business and technology executives.
“AI’s potential for transforming cyber capabilities is clear and far-reaching,” reads a PwC article with highlights from the report.
For example, organizations are prioritizing the use of AI to improve how they allocate cyber budgets; use managed cybersecurity services; and tackle cyber skills gaps.
With regards to respondents' priorities for AI cybersecurity capabilities in the coming year, threat hunting ranked first, followed by agentic AI. Other areas include identity and access management, and vulnerability scanning / vulnerability assessments.
AI security capabilities organizations will prioritize over the next 12 months
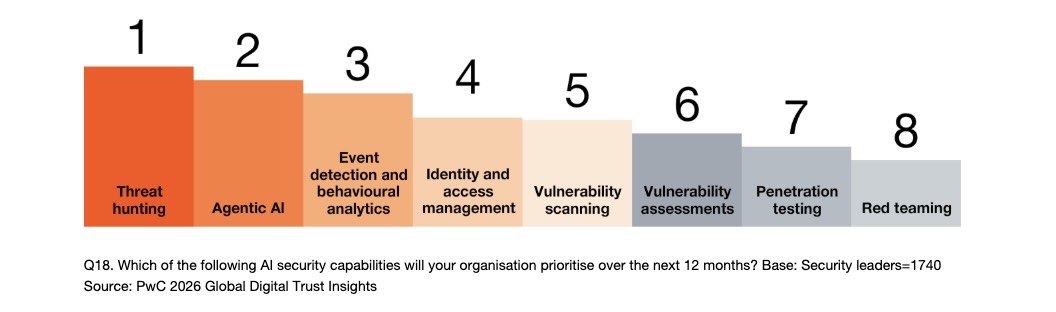
Meanwhile, organizations plan to use agentic AI primarily to boost cloud security, data protection and security operations in the coming year. Other agentic AI priority areas include security testing; governance, risk and compliance; and identity and access management.
“Businesses are recognising that AI agents — autonomous, goal-directed systems capable of executing tasks with limited human intervention — have enormous potential to transform their cyber programmes,” reads the report.
Beyond AI, the report also calls on cyber teams to prioritize prevention over reaction. Proactive work like monitoring, assessments, testing, and training is always cheaper than the crisis-mode alternative of incident response, remediation, litigation, and fines. Yet, only 24% of organizations said they spend “significantly more” on proactive measures.
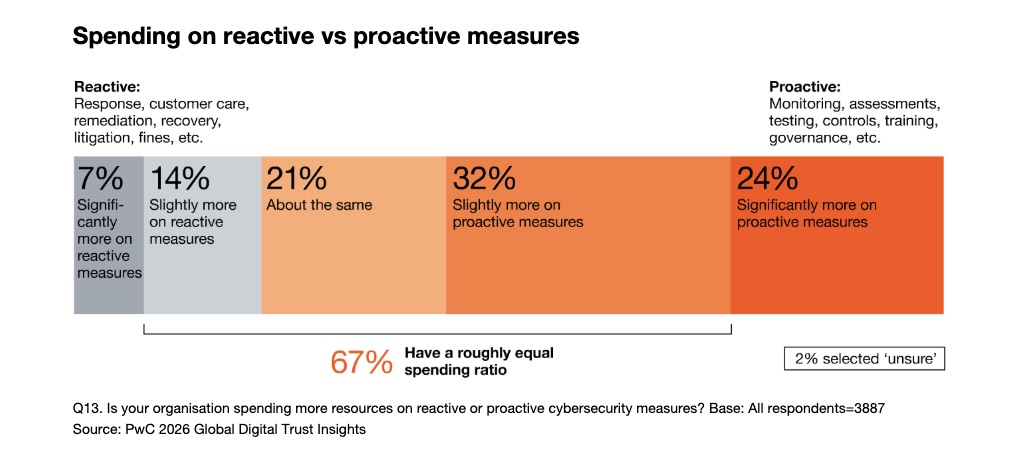
Other topics covered in the report include geopolitical risk; cyber resilience; the quantum computing threat; and the cyber skills gap.
For more information about AI data security, check out these Tenable resources:
- “Harden Your Cloud Security Posture by Protecting Your Cloud Data and AI Resources” (blog)
- “Tenable Cloud AI Risk Report 2025” (report)
- “New Tenable Report: How Complexity and Weak AI Security Put Cloud Environments at Risk” (blog)
- “AI Is Your New Attack Surface” (on-demand webinar)
- “Securing the AI Attack Surface: Separating the Unknown from the Well Understood” (blog)
- “The AI Security Dilemma: Navigating the High-Stakes World of Cloud AI” (blog)
3 - Experts: Patch nasty Oracle zero-day bug – yesterday
Hackers are exploiting a critical zero-day vulnerability in Oracle's E-Business Suite (EBS), and cyber experts including the U.K. National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) are urging organizations to patch affected systems ASAP.
The vulnerability, CVE-2025-61882, exists in the BI Publisher Integration component of Oracle Concurrent Processing in versions 12.2.3 to 12.2.14 of Oracle EBS.
Attackers can exploit the vulnerability remotely without authentication. Once exploited, the vulnerability can grant an attacker the ability to execute code remotely on breached EBS systems and completely compromise them, Oracle said in its security advisory.
Indications about the zero-day exploits surfaced on October 2 via reports that the Cl0p ransomware gang was telling Oracle customers it had swiped data from their EBS systems, as Tenable Research explains in its FAQ blog about CVE-2025-61882.

Exploits of this EBS vulnerability may have started in July or August, according to various reports published this week.
NCSC recommendations for organizations running vulnerable versions of Oracle E-Business Suite include:
- Install the latest update for EBS, which fixes the vulnerability.
- Use the indicators-of-compromise provided by Oracle to assess your exposure.
- Continuously monitor your network and hunt for threats.
- Deploy the EBS following Oracle’s guidance, in order to limit its exposure to the public internet to the minimum level required.
To get more information, read:
- “CVE-2025-61882: Frequently Asked Questions About Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) Zero-Day and Associated Vulnerabilities” (Tenable)
- “Oracle Security Alert Advisory - CVE-2025-61882” (Oracle)
- “Exploitation of Oracle EBS Zero-Day Started 2 Months Before Patching” (SecurityWeek)
- “Clop raid on Oracle E-Business Suite started months ago, researchers warn” (The Register)
- “Google Says Oracle EBS Extortion Campaign Possibly Targeted Thousands, Could Date Back To July” (CRN)
4 - Tenable polls webinar attendees on vulnerability management practices
During our recent webinar “Beyond the endpoint: Exposure management that's proactive,” we polled attendees on their vulnerability management processes and challenges. Check out what they said.
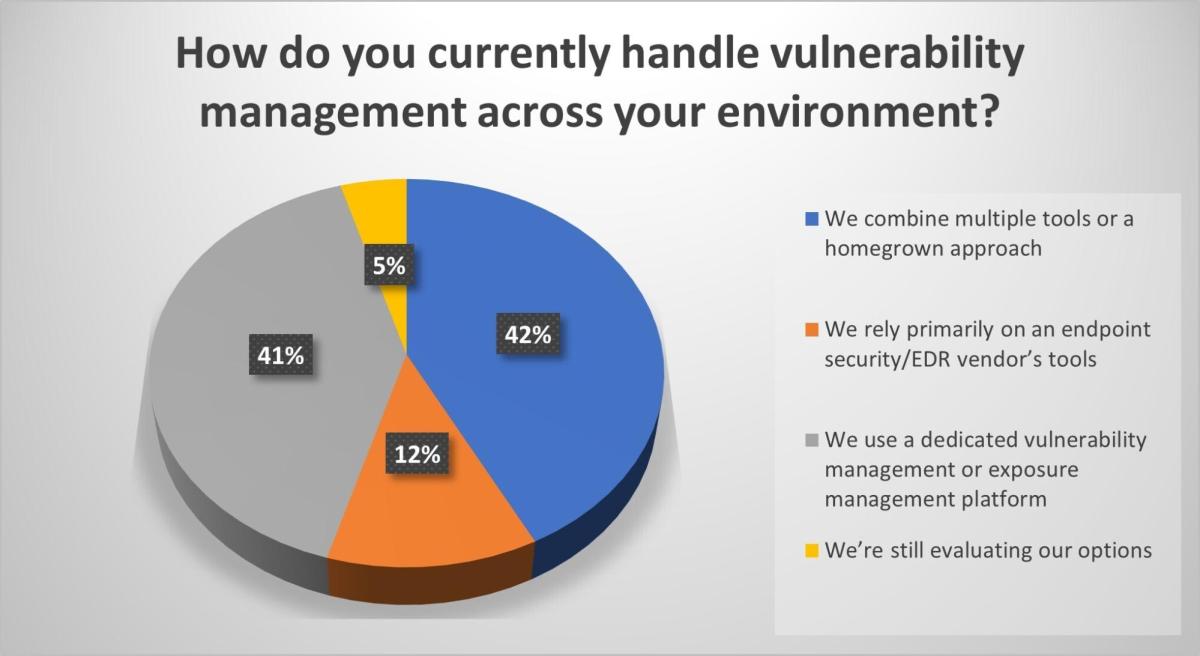
(Source: Tenable webinar poll of 57 respondents, Beyond the Endpoint: Exposure Management That’s Proactive, October 1, 2025)
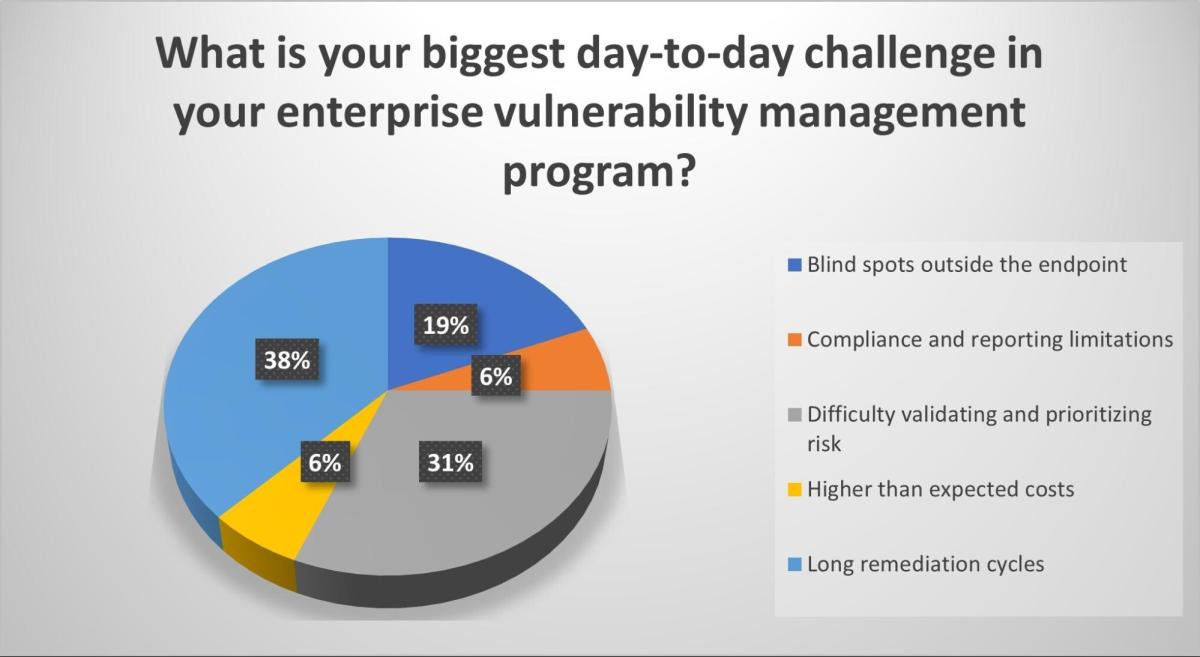
(Source: Tenable webinar poll of 63 respondents, Beyond the Endpoint: Exposure Management That’s Proactive, October 1, 2025)
Watch the webinar on-demand to learn why endpoint-first vulnerability management falls short and how Tenable closes the gaps across IT, cloud, OT, identity and more.
5 - NIST updates security guidance for IoT device manufacturers
This one is for vendors of internet-of-things (IoT) products that are interested in improving the cybersecurity of these wares.
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released a revised draft of its “Foundational Cybersecurity Activities for IoT Product Manufacturers” publication, which seeks to ensure IoT products meet customer security expectations.

Here’s some of what’s new in the updated document, which incorporates feedback from over 400 participants through workshops, written comments and forums:
- The guidance is now better organized for clarity.
- There's a much stronger focus on proactive security, urging makers to think about threat modeling and risk assessments early in the product development lifecycle.
- The guidance also now includes more references to established standards, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, to promote consistency across the industry.
NIST is actively seeking public feedback on this draft until October 31, 2025, and is developing a "worked example" to demonstrate the practical application of the guidance.
“We are committed to advancing IoT cybersecurity and fostering a secure ecosystem for connected product technologies across industries,” reads the NIST blog “Updating Foundational Activities for IoT Product Manufacturers.”
For more information about IoT security, check out these Tenable resources:
- “How to Remediate Risk to Critical OT/IoT Systems without Disrupting Operations” (blog)
- “Blackbox to blueprint: a security leader’s guide to managing OT and IT risk” (ebook)
- “How To Secure Your IT, OT and IoT Assets With an Exposure Management Platform: Complete Visibility with Asset Inventory and Discovery” (blog)
- “The Invisible Bridge: Recognizing The Risk Posed by Interconnected IT, OT and IoT Environments” (webinar)
- “How to Unlock Advanced IoT Visibility for Cyber-Physical Systems” (blog)
6 - Report: Fraudsters are cashing in on weak identity security
Fraud is costing businesses a fortune, as scammers exploit the poor protection of customers’ digital identities.
That’s the urgent message from TransUnion’s report “H2 2025 Update: Top Fraud Trends: Digital Identity Risk Accelerates Fraud Losses” published this week.
“Fraudsters are exploiting every digital touchpoint, from account creation to login and transaction. The financial impact is staggering, and organizations must rethink how they verify identity and secure customer interactions,” Steve Yin, Global Head of Fraud at TransUnion, said in a statement.

Here are key takeaways from the report, which is based on TransUnion proprietary data and surveys of business leaders in six countries and consumers across 18 countries:
- Fraud cost global businesses an average of 7.7% of their annual revenue over the past year – a total of $534 billion.
- The primary drivers of these losses are scams, synthetic identity fraud and account takeover (ATO), with ATO volume surging a whopping 141% since 2021.
- The riskiest stage for digital consumers is new account creation – 8.3% of all attempts in H1 2025 were flagged as fraudulent – driven by a vast supply of stolen credentials.
So what can organizations do about this threat? The report’s recommendations include:
- Adopt a proactive, enterprise-wide approach to fraud prevention. It’s key to unify fragmented systems and data silos to create a holistic view of customer identity.
- Bolster every defensive layer — from identity verification and session monitoring to authentication — with better risk signals and advanced analytics.
- Shift away from simple passwords toward more secure methods like biometrics and one-time passcodes.
As the report bluntly states: “You must assume a security posture that all identity data and credentials presented to your organization are compromised.”
For more information about identity and access management (IAM) security, check out these Tenable blogs:
- “Identity Is the New Battleground: Why Proactive Security Is the Way Forward”
- “Identity-First Security: Mitigating the Cloud’s Greatest Risk Vector”
- “Stronger Cloud Security in Five: Securing Your Cloud Identities”
- “How Identity Plays a Part in 5 Stages of a Cyber Attack”
- “Service Accounts in Active Directory: These OG NHIs Could Be Your Weakest Link”
- Cloud
- Cybersecurity Snapshot
- Risk-based Vulnerability Management


